- Home
- betapharm-co
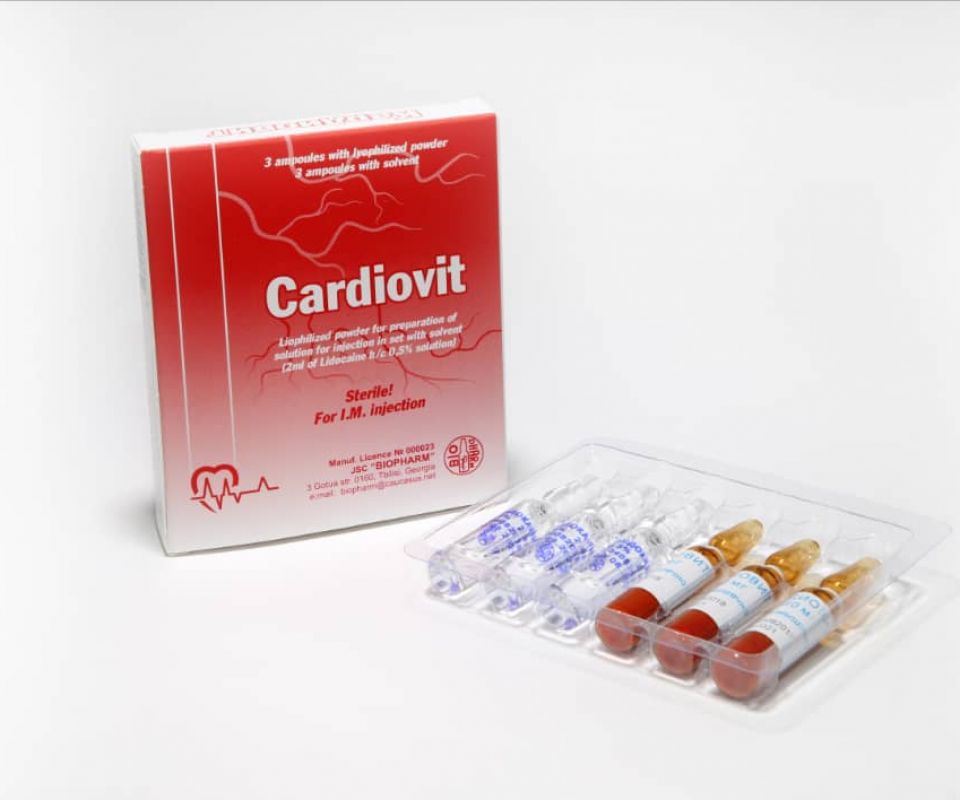
- CARDIOVIT
CARDIOVIT
The drug is a complex of metabolic substances and vitamins. Improves the metabolism and energy supply of tissues.
Trade name of the drug: Cardiovit
Active agents(INN): adenosine triphosphate, cocarboxylase, cyanocobalamin, niacinamide (ATP + cocarboxylase + cyanocobalamine + nicotinamide complex)
Pharmaceutical form: lyophilized powder for preparation of solution for injection.
Formulation:
Each ampoule of the drug (180 mg) contains:
Active moiety: Disodium Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP) – 10 mg, cocarboxylase h/c – 50 mg, nicotinamide – 20 mg, cyanocobalamine – 0,5 mg.
Excipients: glycocine, methylparahydroxybenzoate.
Each ampoule of solvent (2 ml) contains::
Active moiety: lidocaine hydrochloride – 10 mg.
Excipients: water for injection.
Description: Lyophilized dry porous mass of pink color. Hygroscopic.
Pharmacological group: Drug for the adjustment of metabolic processes.
ATC-code: A11JC
Pharmacological properties
Pharmacodynamics
The drug is a complex of metabolic substances and vitamins. Improves the metabolism and energy supply of tissues.
Disodium Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP) – is a derivative of adenosine, stimulates metabolic processes. It has a hypotensive and antiarrhythmic, vasorelaxant action, including on coronary vessels. Under the influence of ATP, there is a decrease in arterial blood pressure, relaxation of smooth muscles, and conduction of nerve impulses improves.
Cocarboxylase is a coenzyme that is formed in the body from thiamine (vitamin B1), which comes from outside. It plays an important role in carbohydrate metabolism; it is part of the carboxylase enzyme, which catalyzes the carboxylation and decarboxylation of α-keto acids. Indirectly promotes the synthesis of nucleic acids, proteins and lipids. Reduces the level of lactic and pyroracemic acid in the body, promotes the absorption of glucose. Improves trophism of nerve tissue.
Cyanocobalamin (vitamin В12) – in the body turns into an active form – adenosylcobalamin or cobamide, which has a high biological activity. Increases protein synthesis in the body and promotes its accumulation. Activates the metabolism of carbohydrates and lipids. Reduces cholesterol in the blood, prevents fatty liver infiltration. It is necessary for the normal functioning of the blood-forming organs, it contributes to the accumulation of compounds that contain sulfhydryl groups in erythrocytes, increasing their resistance to hematolysis. Increases tissues’ regenerating ability. It has a positive effect on the function of the liver and nervous system, arteries.
Nicotinamide – one of the forms of vitamin PP, takes part in the oxidation-reduction process in the cell – regulates tissue respiration, improves carbohydrate and nitrogen metabolism, normalizes lipid metabolism, and reduces the level of atherogenic lipoproteins in the blood.
Pharmakokinetics
Disodium Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP) – After parenteral administration, it penetrates into the cells of organs, where it is split into adenosine and inorganic phosphate with the release of energy. Subsequently, the breakdown products are included in ATP resynthesis.
Cocarboxylase – Quickly absorbed after i/m administration. Penetrates into most body tissues. It undergoes metabolic decomposition. Metabolism products are excreted mainly by the kidneys.
Cyanocobalamin – In the blood, cyanocobalamin binds to transcobalamin I and II, which transport it to the tissues. It is deposited mainly in the liver. Plasma protein binding is 0.9%. Quickly and completely absorbed after i/m and s/c administration. MMC after i/m administration is achieved after 1 h. It is excreted from the liver by bile into the intestine and again absorbed into the blood. It is excreted during normal kidney function – 7-10% by the kidneys, about 50% – through the intestines. With reduced kidney function – 0-7% by the kidneys, 70-100% – through the intestines. Penetrates through the placental barrier into breast milk.
Nicotinamide – It is quickly distributed in all tissues. Penetrates through the placental barrier and into breast milk. It is metabolized in the liver with the formation of nicotinamide-N-methylnicotinamide. It is excreted by the kidneys. T1 / 2 from plasma is about 1.5 hours.
Indications for use
Neuritis and neuralgia of various origins; neuropathies (including diabetes mellitus, pernicious anemia) and angiopathy; lumbago and radiculitis; myalgia and ischialgia; bursitis and tendonitis; coronary heart disease, myocarditis and myocardiopathy; complex treatment of chronic diseases of the cardiovascular system.
Dosage and Administration
A solution of the drug is prepared immediately before administration. Intramuscularly administered. Adults take 1-2 ampoules of the drug per day or every other day. Dosage, duration of treatment and repeated courses as directed by a doctor, depending on the course and severity of the disease.
Contraindications
— hypersensitivity to any component of the drug or solvent;
– cardiovascular diseases (acute heart failure, acute myocardial infarction, uncontrolled arterial hypertension, arterial hypotension, severe forms of bradyarrhythmias, AV block of II-III degree, chronic heart failure (III-IV functional class according to NYHA), cardiogenic shock and others types of shock, QT prolongation syndrome, thromboembolism, hemorrhagic stroke);
– inflammatory diseases of the lungs, COPD, bronchial asthma;
– age up to 18 years;
– hypercoagulation (including with acute thrombosis), erythremia, erythrocytosis;
– peptic ulcer of the stomach or duodenum in the acute phase;
– arthragra;
– hepatitis, hepatic cirrhosis.
The drug should be administered with caution at the time of stenocardia.
Side effects
On the part of the immune system: rarely – allergic reactions (skin rash, difficulty in breathing, anaphylactic shock, Quincke’s edema).
Systemic disturbance and disorders at the administration site: rarely – irritation, pain and heat sensation at the administration site, weakness may occur.
On the part of the nervous system: very rarely – dizziness, headache, induction, confusion.
On the part of the cardiovascular system: very rarely – tachycardia; in some cases bradycardia, arrhythmia; the frequency is unknown – pain in the region of the heart, redness of the skin of the face and upper half of the body with a sensation of pins and needles and heat, “hot flashes”.
On the part of the GIT: very rarely – vomiting, diarrhea.
From the skin and subcutaneous tissues: very rarely – increased sweating, acne, itching, urticaria.
On the part of musculoskeletal and connective tissue: very rarely – convulsions.
In case of the development of severe adverse reactions, the drug is removed.
Drug interactions
In patients using hypoglycemic agents of the biguanide group (metformin), due to impaired absorption of cyanocobalamin from the gastrointestinal tract, a decrease in the concentration of cyanocobalamin in the blood can be observed.
Cyanocobalamin is not compatible with ascorbic acid, salts of heavy metals, thiamine, thiamine bromide, pyridoxine, riboflavin, folic acid.
Simultaneous administration of cyanocobalamin with drugs that increase blood coagulability is prohibited.
In addition, the simultaneous administration of cyanocobalamin with chloramphenicol should be avoided.
Aminoglycosides, salicylates, antiepileptic drugs, colchicine, potassium preparations reduce the absorption of cyanocobalamin.
With the combined use of drugs containing ATP with dipyridamole, the effect of dipyridamole, in particular the vasodilatory effect is enhanced. Dimiridamol enhances the effect of ATP.
Some antagonism is shown with the combined use of the drug with purine derivatives (caffeine, theophylline).
Simultaneous administration with cardiac glycosides in large doses is prohibited, since the risk of developing adverse reactions of the cardiovascular system increases.
With simultaneous administration with xanthinol nicotinate, the effect of the drug is reduced.
Nicotinamide potentiates the effect of sedatives, tranquilizers, as well as antihypertensive drugs.
Special warnings
– Apply the solution of the drug immediately after its preparation! Do not use the drug solution if the color has changed (the color of the freshly prepared solution should be bright red).
– During treatment with the drug, a blood test should be systematically performed. With the development of erythrocytosis and leukocytosis, the dose is reduced or temporarily discontinued. It is also necessary to control blood coagulation and use caution when prone to thrombosis.
–Administration of yanocobalamin in acute thromboembolic diseases is prohibited. Patients with stenocardia should be prescribed with caution and in lower doses (based on up to 120 μg of cyanocobalamin, i.e. 0.5 ml of the drug solution per injection).
– The safety and effectiveness of the drug in children has not been studied.
Pregnancy and lactation
During pregnancy, the drug is administered only if the expected benefit to the mother outweighs the potential risk to the fetus. Breast-feeding should be discontinued during treatment with the drug!
Impact on the ability to drive a car and manage complex mechanisms
In case of side effects on the part of the central nervous system (dizziness, confusion), it is recommended to refrain from driving vehicles and managing other mechanisms.
Overdose
Symptoms: increased side effects of the drug.
Treatment: drug withdrawal and symptomatic therapy.
Packing
Lyophilized powder for the preparation of an injection solution in ampoules complete with a solvent in ampoules.
3 ampoules of the preparation and 3 ampoules of the solvent in a PVC tray with instructions for use in the package.
Storage conditions
In a place inaccessible to children, protected from light at a temperature of no higher than + 250C.
Shelf life
3 years.
Do not use after expiration date.
Dispensing rules
By prescription.